Moon: Our neighbourIntroduction:
moon
Mankind is very fascinated about our space neighbour moon. We, humans, are very curious about the moon since our ancient times. Moon is our natural satellite. It is revolving around us. Moon is a dry and dusty celestial object and the cause of tidal activities on earth.Some facts:
- The moon is nearly 384,400 km from earth, revolving around us.
- It is the fifth-largest moon in our solar system.
- The average distance between the earth to the moon is 384403 kilometres (238857 miles).
- The moon orbits the earth every 27.3 days.
- The moon Huygens is the tallest mountain on the moon it is about 4700 meters.
- The side that we see from the earth is the near side while the other sides are called the far sides.
- The Soviet Union’s Luna program featured the first successful landing of an unmanned spacecraft on the surface of the Moon in 1966.
- The USA’s NASA Apollo 11 mission in 1969 was the first manned Moon landing.
- The first person on the moon was Neil Armstrong, Buzz Aldrin, Michael Collins.
Structure of Moon:Moon is a barren rocky sphere having the mass of 7.34767309 × 1022 kilograms. The moon having lesser mass in comparison to Earth, so it has gravitational acceleration is about one-sixth of earth's gravitational acceleration. If you want to lose weight you better go to moon and take reading there.
India’s Moon
missions:
India had launched several missions on
the moon. The first one is Chandrayaan-1 which launched in 2008 by ISRO (Indian
Space Research Organisation) from Indian spaceport Shreeharikota. It was launched
from the PSLV-C11 rocket. It consists of an orbiter and an impactor. It was a successful
mission. The main findings of the missions are the presence of ice on poles and the
presence of helium-3.
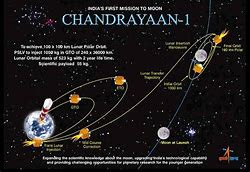 |
| Chandrayaan-1 source: Indiatimes |
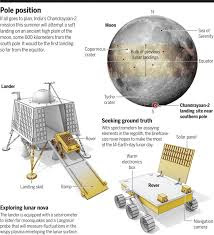 |
| info-graphics of chandrayaan-2 source: earthsky.org |
It consists of three probes the Vikram (lander), Pragyan (rover), and one orbiter. The orbiter was a success but the lander at the time of landing the communication link was broken, leads to the crash of it. ISRO
accepts the failure and starts investigating the reason for the failure. The
orbiter starts sending pictures of the moon.
 |
| The GSLV Mark III (Bahubali) the rocket used for launching of Chandrayaan-2 source: indiatoday |









0 Comments